An example showing how to do optimization with general constraints using SLSQP and cobyla.
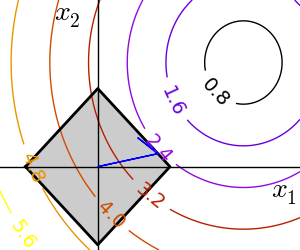
Script output:
Optimization terminated successfully. (Exit mode 0)
Current function value: 2.47487373504
Iterations: 5
Function evaluations: 20
Gradient evaluations: 5
Python source code: plot_non_bounds_constraints.py
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from scipy import optimize
x, y = np.mgrid[-2.03:4.2:.04, -1.6:3.2:.04]
x = x.T
y = y.T
pl.figure(1, figsize=(3, 2.5))
pl.clf()
pl.axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
contours = pl.contour(np.sqrt((x - 3)**2 + (y - 2)**2),
extent=[-2.03, 4.2, -1.6, 3.2],
cmap=pl.cm.gnuplot)
pl.clabel(contours,
inline=1,
fmt='%1.1f',
fontsize=14)
pl.plot([-1.5, 0, 1.5, 0, -1.5],
[ 0, 1.5, 0, -1.5, 0], 'k', linewidth=2)
pl.fill_between([ -1.5, 0, 1.5],
[ 0, -1.5, 0],
[ 0, 1.5, 0],
color='.8')
pl.axvline(0, color='k')
pl.axhline(0, color='k')
pl.text(-.9, 2.8, '$x_2$', size=20)
pl.text(3.6, -.6, '$x_1$', size=20)
pl.axis('tight')
pl.axis('off')
# And now plot the optimization path
accumulator = list()
def f(x):
# Store the list of function calls
accumulator.append(x)
return np.sqrt((x[0] - 3)**2 + (x[1] - 2)**2)
def constraint(x):
return np.atleast_1d(1.5 - np.sum(np.abs(x)))
optimize.fmin_slsqp(f, np.array([0, 0]),
ieqcons=[constraint, ])
accumulated = np.array(accumulator)
pl.plot(accumulated[:, 0], accumulated[:, 1])
pl.show()
Total running time of the example: 0.08 seconds ( 0 minutes 0.08 seconds)